Power electronics Device and their symbols plus V -I characteristic
1) Diode
Two types of diode
i) Germanium
Germanium diodes have the advantage of an intrinsically low forward voltage drop, typically 0.3 volts; this low forward voltage drop results in a low power loss and more efficient diode, making it superior in many ways to the silicon diode.
ii) Silicon
A diode is an electrical switch commonly made of semiconductor material, such as silicon. It consists of two terminals: positive (anode) and negative (cathode). It is often used as a rectifier, which is a device that converts AC to DC with current flowing in one direction.
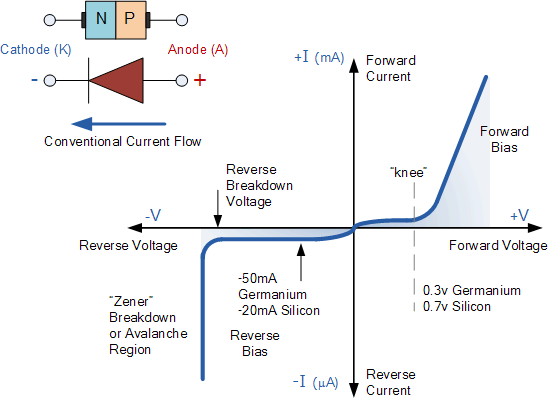
V-I Characteristic of Diode
Sub type of Diode
schottky Diode
A Schottky diode is one type of electronic component, which is also known as a barrier diode. It is widely used in different applications like a mixer, in radio frequency applications, and as a rectifier in power applications. It's a low voltage diode. The power drop is lower compared to the PN junction diodes.
Shockley Diode
Light -emitting Diode
An LED is electronic device that emits light when sufficient current flows throughout the object. LED is very heavily doped.
Photo Diode
A vacuum tube, an electron tube, valve (British usage) or tube (North America),is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve uses the phenomenon of thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode and is used for a number of fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplification and current rectification. Non-thermionic types, such as a vacuum phototube however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube.
The simplest vacuum tube, the diode, invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—from the cathode to the anode. Adding one or more control grids within the tube allows the current between the cathode and anode to be controlled by the voltage on the grids.
I used data for this blog from internet and random selection so if any issue related to licences or copy right or mention the credit please contact me.
I am engineer not artist or digital creator i'm just beginner here not aware many rules










No comments:
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt comment me.